Call or Chat 24/7 at (866) 497-2736
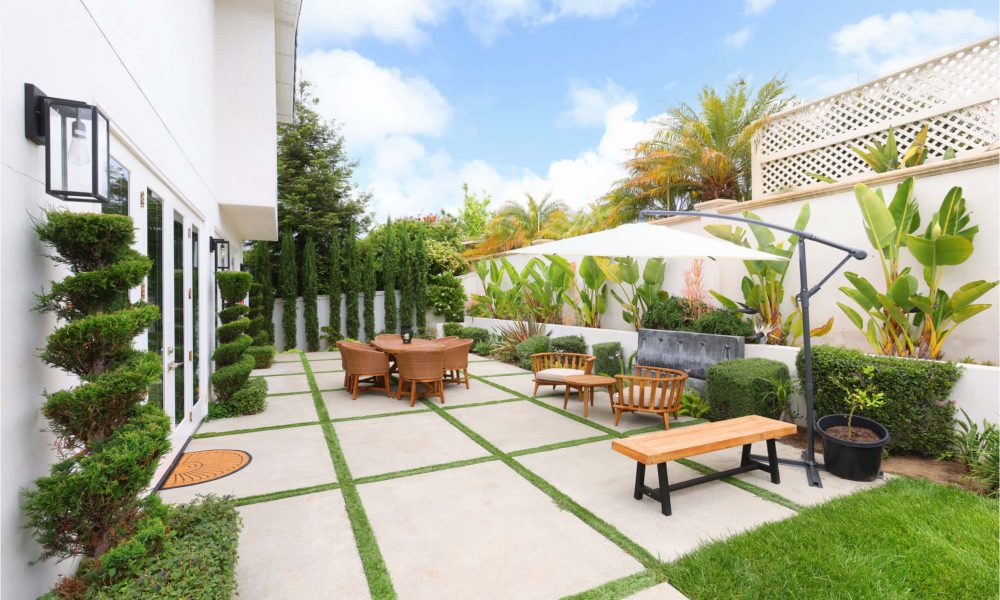
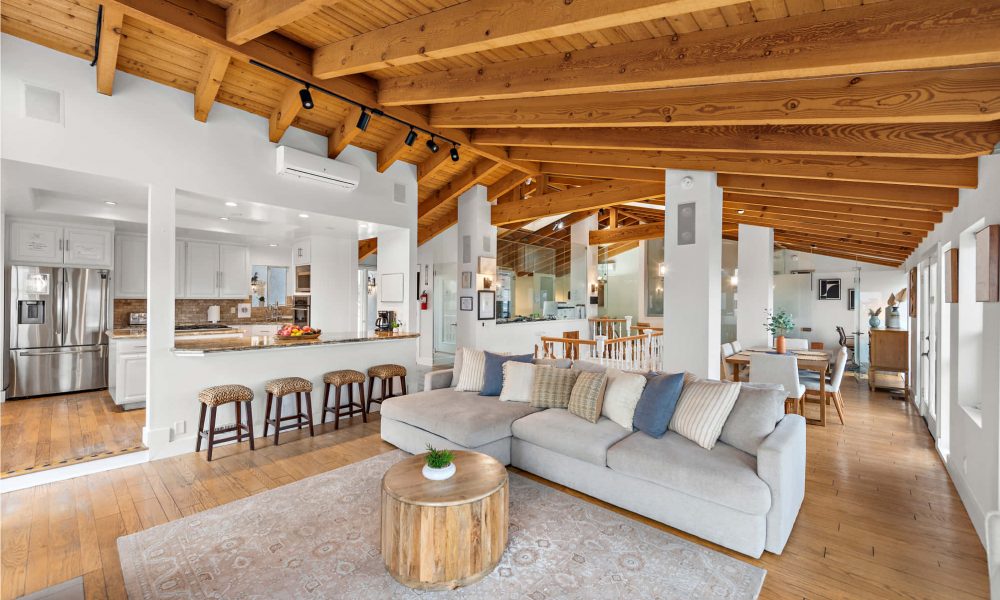
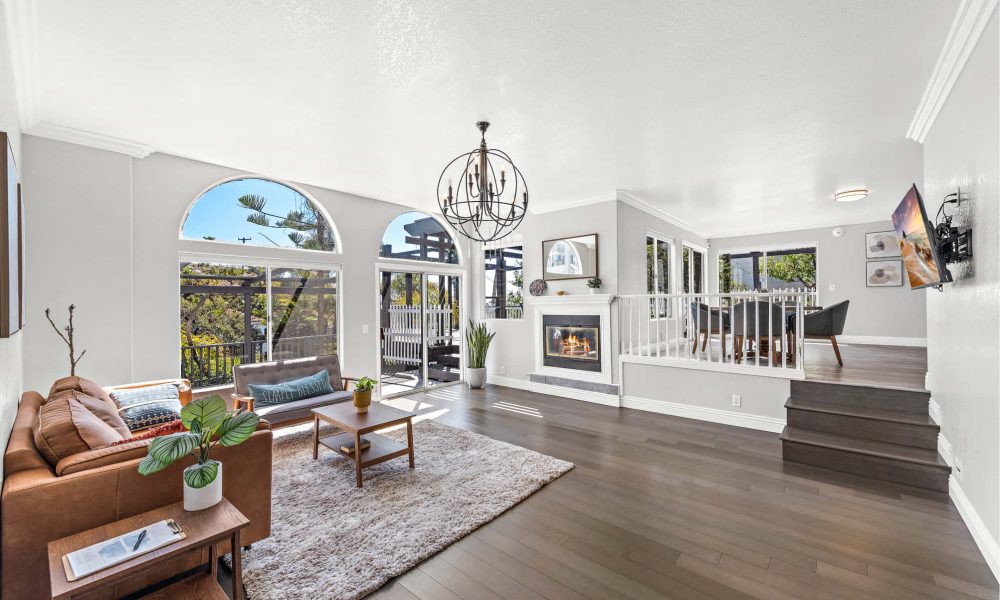
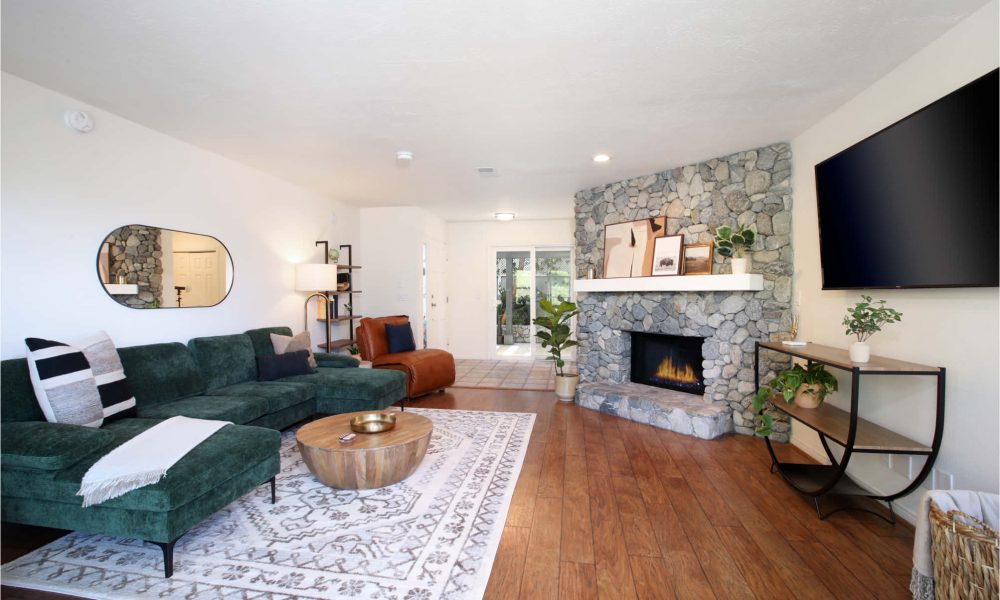
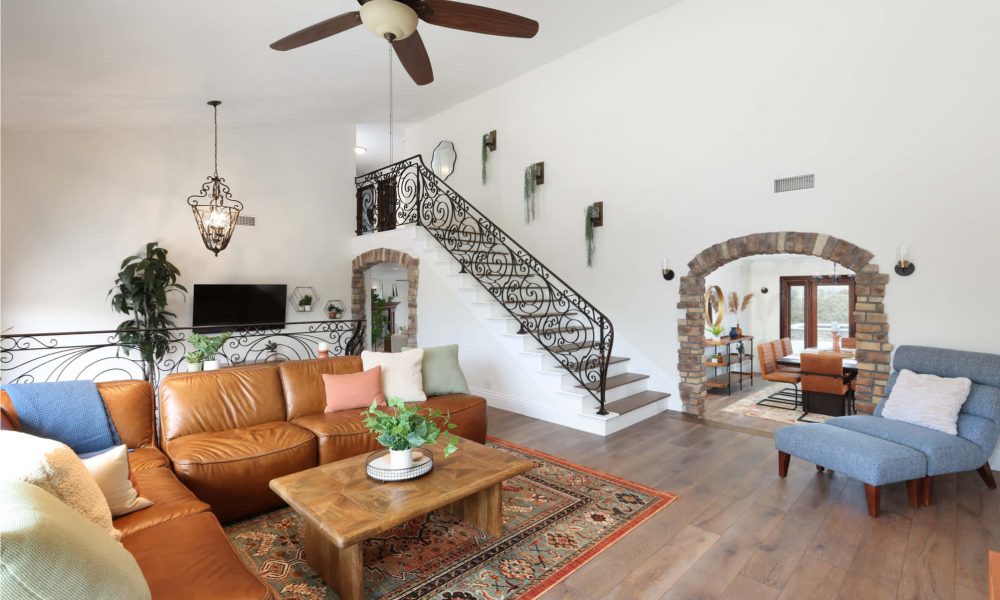
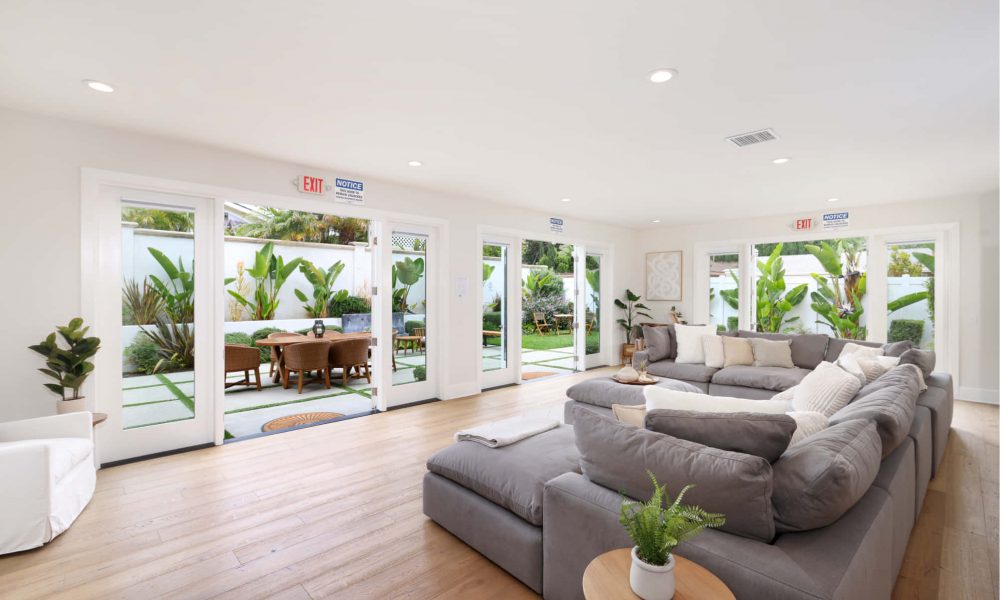
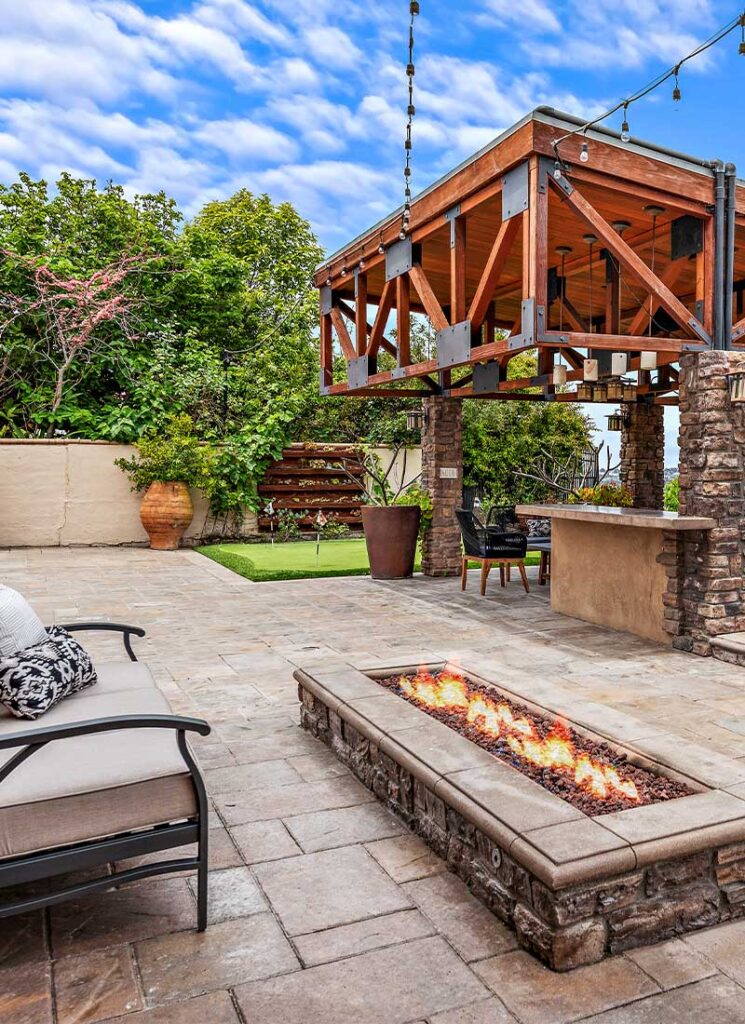
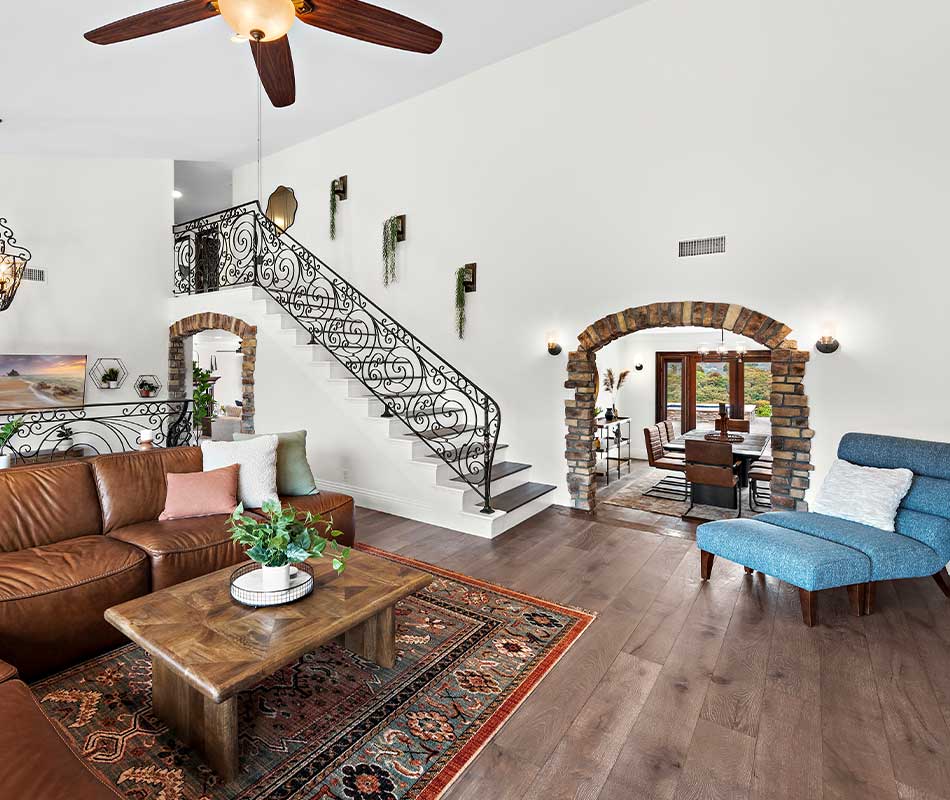












ALTER FACILITIES
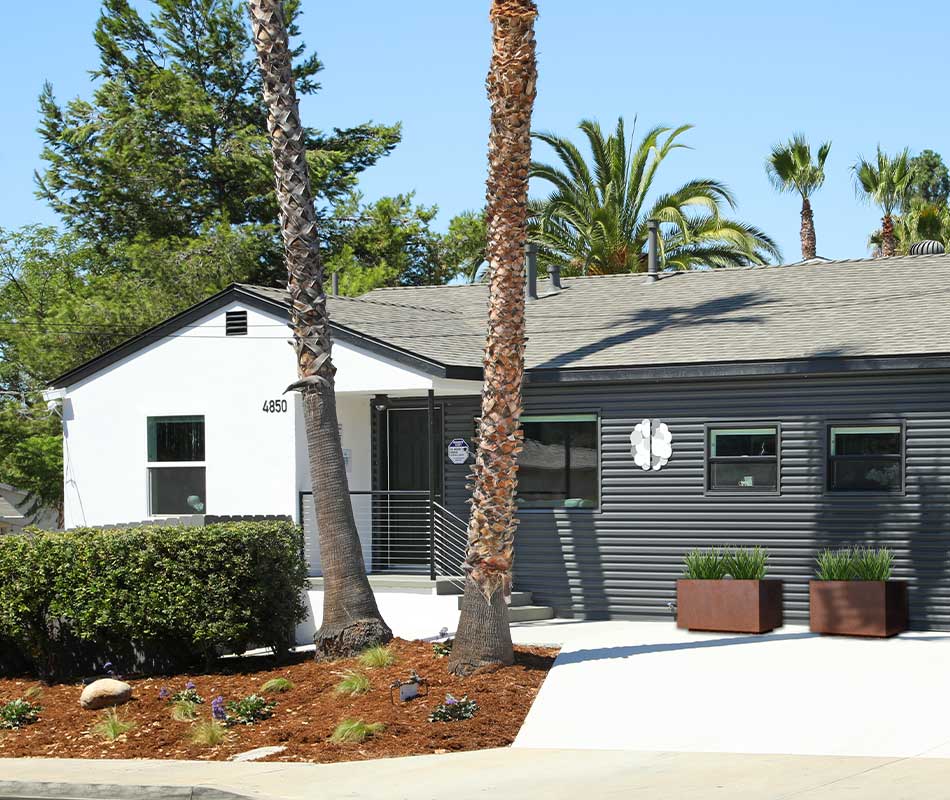
A Crisis Stabilization facility is located in San Juan Capistrano, CA. It is an alternative to inpatient hospitalization. This facility has psychiatrists, registered nurses, and mental health crisis counselors for individuals experiencing a mental health crisis.


ALTER FACILITIES
Alter’s Crisis Stabilization facility is an alternative to inpatient hospitalization. Facility has psychiatrists, registered nurses and mental health crisis counselors for individuals experiencing a mental health crisis.


ALTER FACILITIES
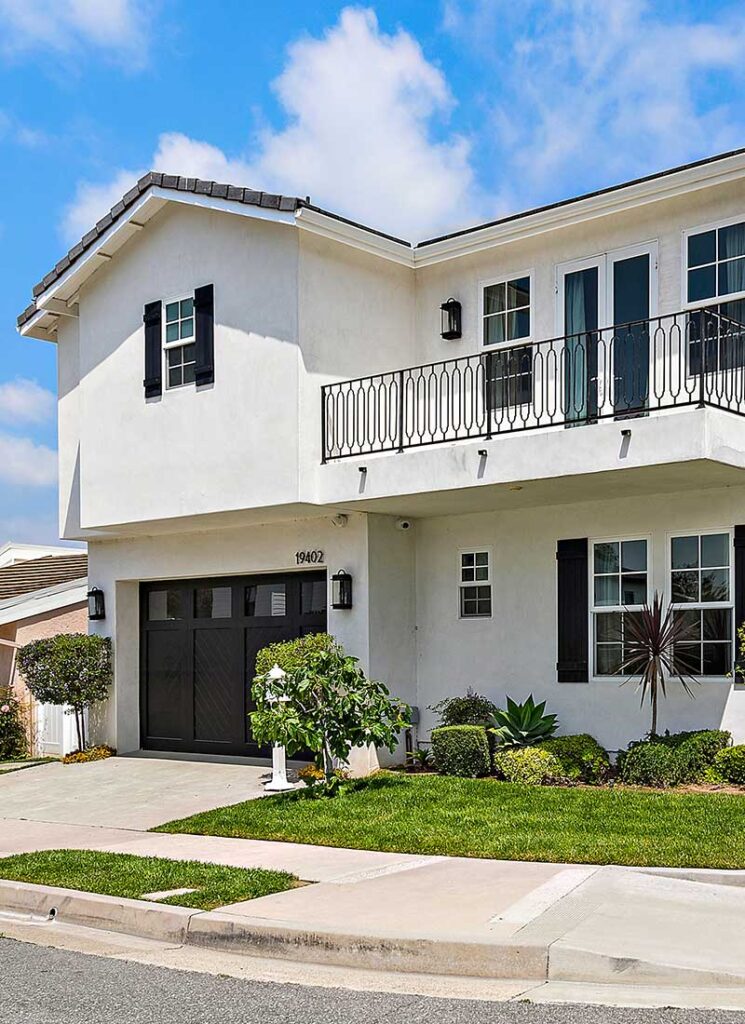
Residential treatment for primary mental health conditions and offer autism-informed care in a 6-bed residence. Personalized treatment and care for neurodivergent individuals.
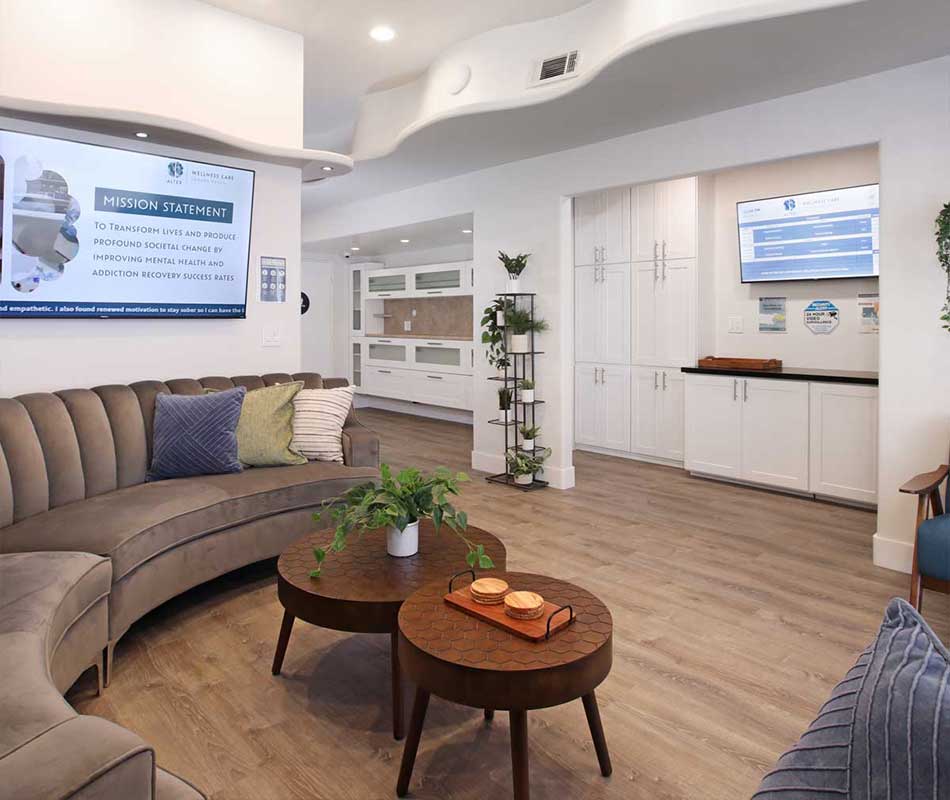


ALTER FACILITIES
Alter Wellness Care offers structured clinical programs at the PHP, IOP, and OP levels designed to provide individualized treatment focused on maintaining and improving functional abilities.
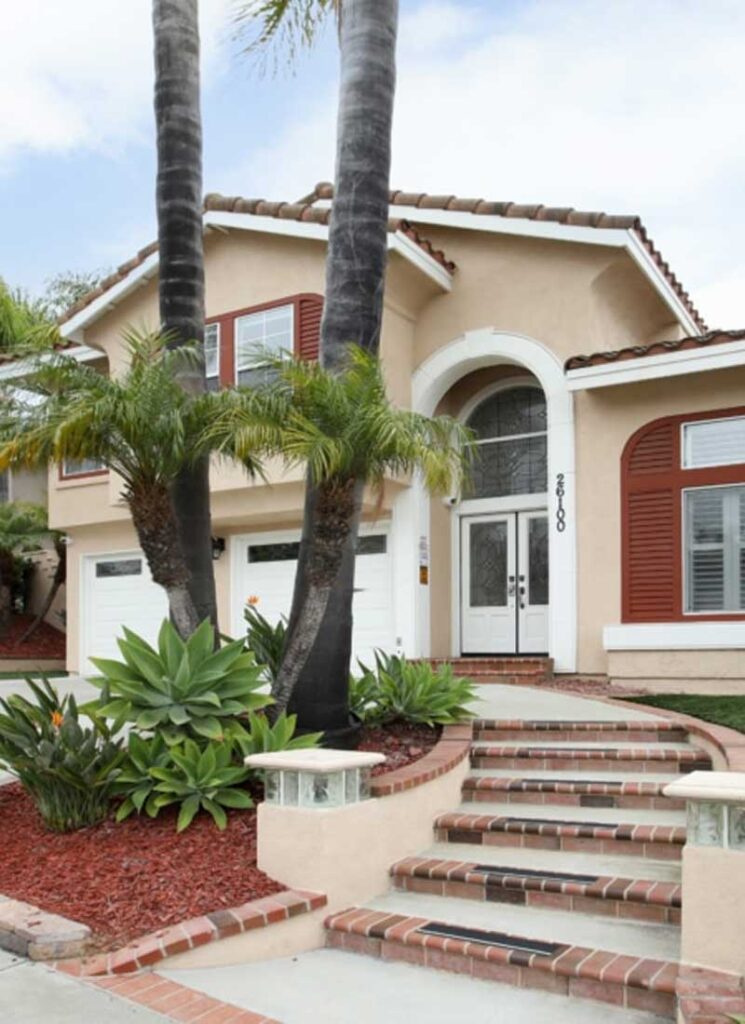


ALTER FACILITIES
This 6-bed residential mental health facility specializes in primary mental health and co-occurring disorder treatment. Features a 24/7 support and multidisciplinary treatment team.
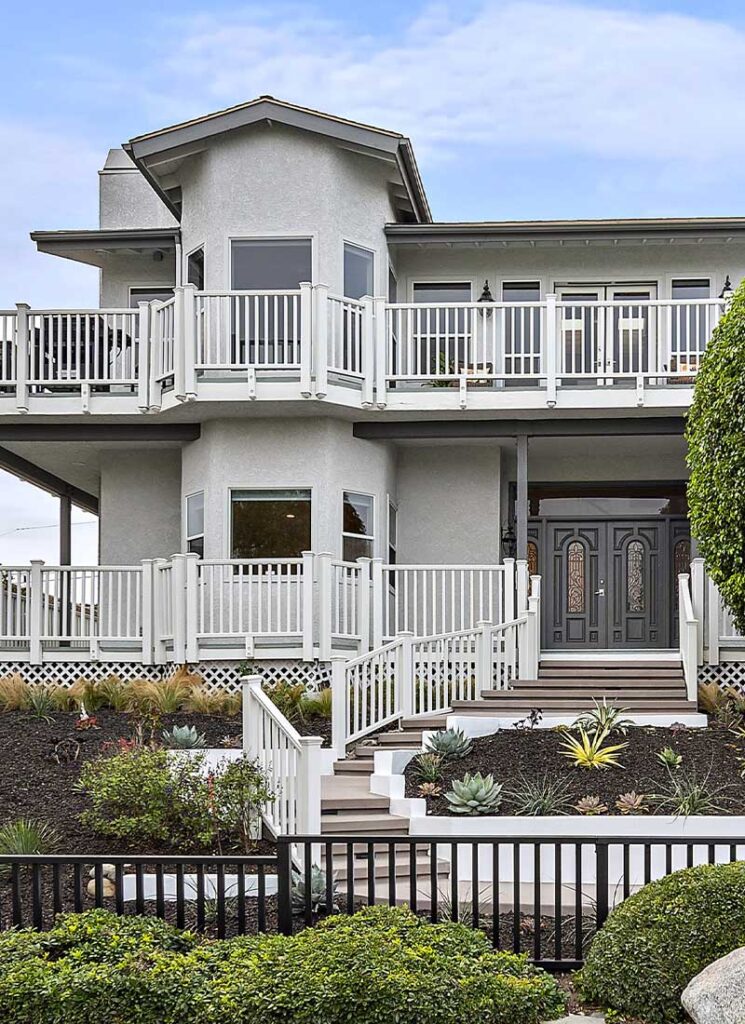
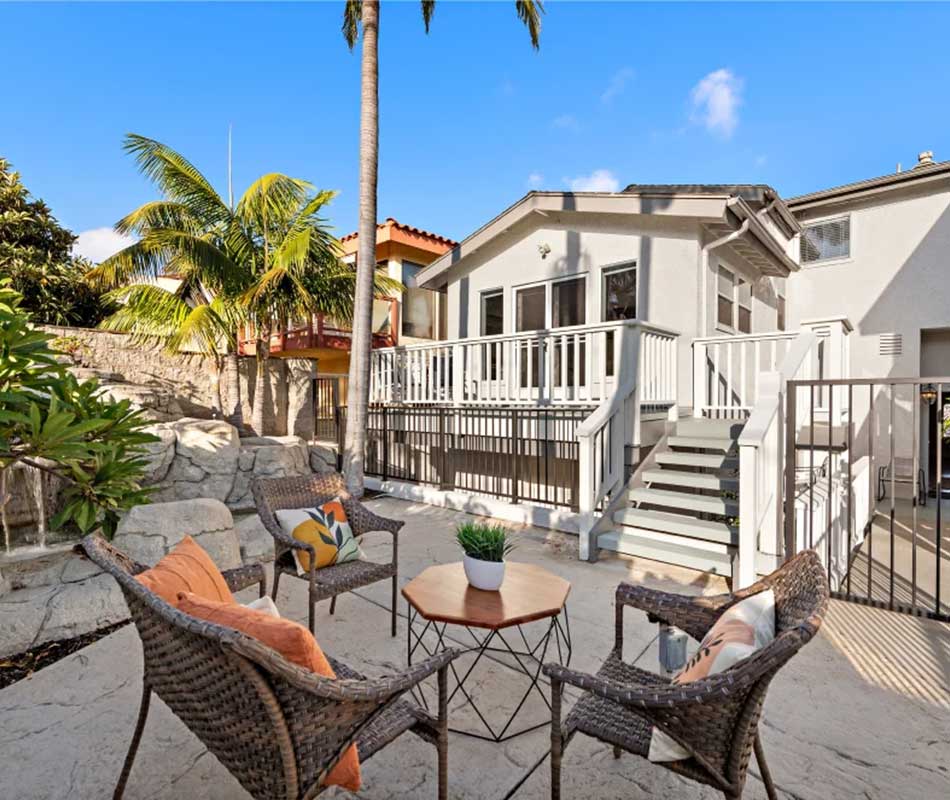


ALTER FACILITIES
Dana Point is an inpatient treatment environment for alcohol and drug addiction. Our treatment team will evaluate your medical health, mental health and substance use history in order to design an individualized drug or alcohol rehab plan for you.









Alter Behavioral Health is a premiere resource for mental health and addiction treatment serving adults nationwide. Our clients receive personalized care overseen by our psychiatry team and doctorate or master’s-level clinicians. We maintain a small number of clients in each of our homes to provide an intimate treatment environment. This allows us to service a wide range of clinical concerns and still provide a very individualized treatment experience. Our treatment offerings change lives through our focus on evidence-based clinical treatment and compassionate care.
When an individual lives with mental illness, it can have a devastating impact on all aspects of their life if they don’t seek treatment. Depending on the type of disorder an individual has, they might not be able to develop healthy relationships, maintain employment, or succeed in school. They may also turn to the use of drugs or alcohol in an attempt to self-medicate and subsequently suffer from declining physical health.
Regardless of which Alter treatment facility an individual enters, they can expect to work in close collaboration with dedicated professionals who are skilled at employing a wide range of therapies and treatment techniques that provide the most focused care and best prepares them for continued success. At Alter’s treatment facilities, the emphasis is not merely on alleviating symptoms, but on identifying and addressing the underlying issues and potential co-occurring disorders that have been preventing the individuals in treatment from living their best lives.


Contact our admissions team for a free consultation or more details about any of Alter’s programs.
Or Call Us 24/7 at


TALK TO ADMISSIONS
Or Call Us 24/7 at

1,911+
Clients Helped Since 2021
130,000+
Lives Impacted
Alter received a grant from CalHope.org to provide mental health care, life guidance, and emotional support available to California residents, free of charge. www.BeWellLine.com
97%
Client Satisfaction
We survey all of the clients who participate in treatment with us. In 2023, over 97% clients said they would return to our care.
Check out the latest blogs and news from Alter Behavioral Health
Suicide and crisis hotlines provide help to those in need. Contact a hotline if you need support for yourself or need help supporting a friend. If you’re concerned about someone, please encourage the person to contact a hotline as well.
for emergency services
for emergency services
for LGBT youth, friends, & family members
for U.S. service members, veterans, & their families
We are on a mission to improve the lives of people with mental health conditions.
34270 Pacific Coast Hwy
3rd Floor
Dana Point, CA 92629
Questions? Call now to speak confidentially with an admissions counselor.
We understand that choosing the right program can be challenging. By filling out this contact form, our experienced team will review your information and reach out to guide you throughout the next steps.
Mental Health Treatment
Substance Mis-use Disorder Treatment
Call Us 24/7
Other Alter Sites
bewellline.com
mindfuli.com
alterdlifepodcast.com